Press release
Engineering Multivalent Antibodies for Specificity and Potency
The engineering of multivalent antibodies represents a cutting-edge approach in the development of highly specific and potent therapeutics. These antibodies, designed to bind multiple antigens or epitopes simultaneously, offer significant advantages over traditional monoclonal antibodies, providing enhanced efficacy and reducing the likelihood of resistance. The focus on specificity and potency in multivalent antibody design opens new avenues for treating complex diseases, particularly in oncology, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders.
Download Bispecific, Trispecific and Tetraspecific Antibodies Report:
https://www.kuickresearch.com/ccformF.php?t=1721642510
The core strength of multivalent antibodies lies in their ability to target multiple antigens simultaneously. This multi-target approach allows for a more comprehensive attack on disease-causing agents, significantly improving therapeutic outcomes. For instance, in cancer therapy, tumors often exhibit heterogeneity, with different cells expressing various antigens. Monoclonal antibodies targeting a single antigen may leave some cancer cells untouched, leading to recurrence and resistance. In contrast, multivalent antibodies can simultaneously bind to multiple tumor-associated antigens, ensuring a broader and more effective treatment.
The design of multivalent antibodies involves sophisticated engineering techniques to achieve the desired specificity and potency. One of the key strategies is the development of bispecific antibodies, which have two different antigen-binding sites. These bispecific antibodies can link a tumor cell to an immune effector cell, such as a T cell, thereby enhancing the immune system's ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells. This dual-targeting mechanism not only improves the immune response but also minimizes off-target effects, increasing the therapy's safety and efficacy.
Another advanced approach is the creation of tetravalent or higher-order multivalent antibodies. These molecules can bind multiple antigens on a single or multiple cells, amplifying their therapeutic effects. The increased binding avidity, resulting from multiple binding sites, enhances the overall potency of the antibody. This higher binding strength ensures that the antibodies remain attached to their targets for longer periods, improving their effectiveness in eliminating disease-causing cells.
The engineering process for multivalent antibodies also involves optimizing the molecular structure to enhance stability and reduce potential immunogenicity. Advances in protein engineering and bioinformatics have enabled the precise modification of antibody structures to achieve these goals. High-throughput screening technologies are employed to identify the most effective antibody candidates from large libraries, ensuring that only the best-performing molecules advance to clinical development.
One of the notable successes in this field is the bispecific antibody blinatumomab, which has shown significant efficacy in treating acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blinatumomab works by simultaneously binding to CD19 on leukemia cells and CD3 on T cells, effectively directing the T cells to kill the leukemia cells. This mechanism exemplifies the potential of multivalent antibodies to provide highly specific and potent therapeutic effects.
Beyond oncology, multivalent antibodies hold promise in treating infectious diseases. By targeting multiple viral antigens, these antibodies can provide broad-spectrum protection against various strains of a virus. This capability is particularly valuable in combating diseases with high mutation rates, such as influenza and HIV. In autoimmune disorders, multivalent antibodies can target multiple disease pathways simultaneously, offering more comprehensive disease management and potentially leading to more durable remissions.
The future of multivalent antibody engineering is bright, with ongoing research focused on refining their design and expanding their applications. Integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into the development process is expected to accelerate the discovery of optimal antibody configurations and streamline the development timeline. These technologies can predict potential challenges and identify the best candidates more efficiently, enhancing the overall success rate of new therapeutics.
However, challenges remain in the manufacturing and regulatory aspects of multivalent antibodies. The complexity of producing these sophisticated molecules requires advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure consistency and quality. Additionally, potential immunogenicity and the need for rigorous regulatory approvals pose hurdles that must be carefully managed. Nonetheless, the scientific community is optimistic that these challenges can be overcome through continued innovation and collaboration.
In conclusion, the engineering of multivalent antibodies for specificity and potency represents a transformative advancement in therapeutic development. By leveraging their ability to target multiple antigens simultaneously, these antibodies offer a powerful tool for treating complex diseases. As research and technology continue to advance, multivalent antibodies are poised to become a critical component of next-generation therapeutics, providing new hope for improved patient outcomes and enhanced healthcare delivery.
KuicK Research
Delhi
India
Kuick Research is a market research and analytics company that provides targeted information for critical decisions at business, product and service levels. We are quick, predictive and known by the recommendations we have made in the past. Our result-oriented research methodology offers understanding of multiple issues in a short period of time and gives us the capability to keep you full with loads of practical ideas. By translating research answers into strategic insight and direction, we not only rate the success potential of your products and/or services, but also help you identify the opportunities for growth in new demographies and find ways to beat competition.
Download Bispecific, Trispecific and Tetraspecific Antibodies Report:
https://www.kuickresearch.com/ccformF.php?t=1721642510
The core strength of multivalent antibodies lies in their ability to target multiple antigens simultaneously. This multi-target approach allows for a more comprehensive attack on disease-causing agents, significantly improving therapeutic outcomes. For instance, in cancer therapy, tumors often exhibit heterogeneity, with different cells expressing various antigens. Monoclonal antibodies targeting a single antigen may leave some cancer cells untouched, leading to recurrence and resistance. In contrast, multivalent antibodies can simultaneously bind to multiple tumor-associated antigens, ensuring a broader and more effective treatment.
The design of multivalent antibodies involves sophisticated engineering techniques to achieve the desired specificity and potency. One of the key strategies is the development of bispecific antibodies, which have two different antigen-binding sites. These bispecific antibodies can link a tumor cell to an immune effector cell, such as a T cell, thereby enhancing the immune system's ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells. This dual-targeting mechanism not only improves the immune response but also minimizes off-target effects, increasing the therapy's safety and efficacy.
Another advanced approach is the creation of tetravalent or higher-order multivalent antibodies. These molecules can bind multiple antigens on a single or multiple cells, amplifying their therapeutic effects. The increased binding avidity, resulting from multiple binding sites, enhances the overall potency of the antibody. This higher binding strength ensures that the antibodies remain attached to their targets for longer periods, improving their effectiveness in eliminating disease-causing cells.
The engineering process for multivalent antibodies also involves optimizing the molecular structure to enhance stability and reduce potential immunogenicity. Advances in protein engineering and bioinformatics have enabled the precise modification of antibody structures to achieve these goals. High-throughput screening technologies are employed to identify the most effective antibody candidates from large libraries, ensuring that only the best-performing molecules advance to clinical development.
One of the notable successes in this field is the bispecific antibody blinatumomab, which has shown significant efficacy in treating acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blinatumomab works by simultaneously binding to CD19 on leukemia cells and CD3 on T cells, effectively directing the T cells to kill the leukemia cells. This mechanism exemplifies the potential of multivalent antibodies to provide highly specific and potent therapeutic effects.
Beyond oncology, multivalent antibodies hold promise in treating infectious diseases. By targeting multiple viral antigens, these antibodies can provide broad-spectrum protection against various strains of a virus. This capability is particularly valuable in combating diseases with high mutation rates, such as influenza and HIV. In autoimmune disorders, multivalent antibodies can target multiple disease pathways simultaneously, offering more comprehensive disease management and potentially leading to more durable remissions.
The future of multivalent antibody engineering is bright, with ongoing research focused on refining their design and expanding their applications. Integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning into the development process is expected to accelerate the discovery of optimal antibody configurations and streamline the development timeline. These technologies can predict potential challenges and identify the best candidates more efficiently, enhancing the overall success rate of new therapeutics.
However, challenges remain in the manufacturing and regulatory aspects of multivalent antibodies. The complexity of producing these sophisticated molecules requires advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure consistency and quality. Additionally, potential immunogenicity and the need for rigorous regulatory approvals pose hurdles that must be carefully managed. Nonetheless, the scientific community is optimistic that these challenges can be overcome through continued innovation and collaboration.
In conclusion, the engineering of multivalent antibodies for specificity and potency represents a transformative advancement in therapeutic development. By leveraging their ability to target multiple antigens simultaneously, these antibodies offer a powerful tool for treating complex diseases. As research and technology continue to advance, multivalent antibodies are poised to become a critical component of next-generation therapeutics, providing new hope for improved patient outcomes and enhanced healthcare delivery.
KuicK Research
Delhi
India
Kuick Research is a market research and analytics company that provides targeted information for critical decisions at business, product and service levels. We are quick, predictive and known by the recommendations we have made in the past. Our result-oriented research methodology offers understanding of multiple issues in a short period of time and gives us the capability to keep you full with loads of practical ideas. By translating research answers into strategic insight and direction, we not only rate the success potential of your products and/or services, but also help you identify the opportunities for growth in new demographies and find ways to beat competition.
Permanent link to this press release:
Copy
Please set a link in the press area of your homepage
to this press release on woodPRI. woodPRI disclaims liability for any content contained in
this release.
Recommend
/newsMicroencapsulation Market Deep Analysis on Key Players - Dow Corning, Encapsys, Syngenta Crop Protection, Evonik Industries, 3M and Bayer
Market Study Report Adds Global Microencapsulation Market Size, Status and Forecast 2024 added to its database. The report provides key statistics on the current state of the industry and other analytical data to understand the market.
Extensive research is required for choosing the appropriate cor...

/newsGermany Airbag Market Size 2023: Global Share, Industry And Report Analysis By 2030 | Hyundai Mobis Co., Ltd. Key Safety Systems, Inc. Robert Bosch GmbH
Germany airbag market is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 6% during the forecast period. Germany Airbag Market research report refers to gathering and analyzing significant market data serve as best medium for various industry players to launch novel product or service. It is vital for key firms...
/newsSecurities Brokerages And Stock Exchanges Market Outlook 2021: Big Things are Happening
A new intelligence report released by HTF MI with title "Global Securities Brokerages And Stock Exchanges Market Survey & Outlook" is designed covering micro level of analysis by Insurers and key business segments, offerings and sales channels. The Global Securities Brokerages And Stock Exchange...

/newsRenewable Chemicals Market Emerging Trends and Competitive Landscape Forecast to 2028
The renewable chemicals market was valued at US$ 80,566.30 million in 2021 and is projected to reach US$ 1,76,750.76 million by 2028 it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.9% from 2021 to 2028. The research report focuses on the current market trends, opportunities, future potential of the market, a...
/newsHow Coronavirus is Impacting Cold Brew Coffee, Global Market Volume Analysis, Size, Share and Key Trends 2020-2026
"Market Latest Research Report 2020:
Los Angles United States, February 2020: The Cold Brew Coffee market has been garnering remarkable momentum in the recent years. The steadily escalating demand due to improving purchasing power is projected to bode well for the global market. QY Research's lates...
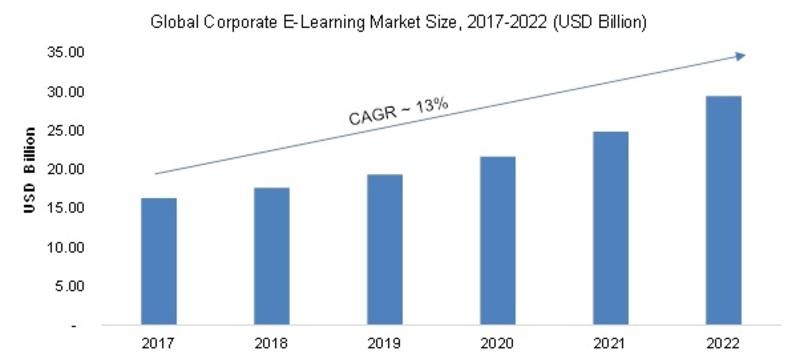
/newsCorporate E-Learning Market - Global Industry Size, Share, Key Players Analysis that are Infor, SkillSoft Corporation, Adrenna, CERTPOINT Systems and others with Regional Forecast to 2022
Overview:
E-Learning is used to enhance the learning procedures for newer job requirements and to make employees sound about the internal and external changes in the market and respective organizations. This method has created considerable differences in the ways of training and developing employee...
