Press release
Understanding the Regulation of Stablecoins Under the MiCA Regime: A Compliance Guide By PayRate42 !
The EU's Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation represents a significant step for crypto regulation, particularly concerning the oversight of stablecoins, such as USDT. As compliance officers, it's crucial to understand the regulatory landscape under MiCA, the roles of key regulatory bodies such as the European Banking Authority (EBA) and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), and the reasons driving this regulatory interest.
MiCA and Stablecoins: An Overview
MiCA aims to provide a comprehensive regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies and digital assets within the EU, enhancing market integrity and consumer protection. Stablecoins, classified under MiCA as either asset-referenced tokens (ARTs) or e-money tokens EMTs), face specific regulatory requirements to ensure their stability and reliability. These requirements include maintaining sufficient reserves, regular audits, transparency in operations, and adherence to consumer protection standards.
Roles of EBA and ESMA
EUROPEAN BANKING AUTHORITY (EBA)
The EBA plays a pivotal role in the supervision of significant stablecoins - ARTs and EMTs - under MiCA. When stablecoins surpass a specific adoption threshold, determined by quantitative and qualitative indicators, they fall under the direct supervision of the EBA rather than national authorities. The EBA's responsibilities include:
Ensuring Adequate Reserves: The EBA ensures that stablecoin issuers maintain adequate reserves to back the value of their tokens, safeguarding against insolvency risks.
Conducting Audits: Regular audits are mandated to verify the integrity of the stablecoin reserves and operational practices.
Enforcing Transparency: The EBA requires issuers to provide detailed reports and disclosures, promoting transparency and protecting investors.
EUROPEAN SECURITIES AND MARKETS AUTHORITY (ESMA)
While the EBA focuses on the financial stability and reserve management of stablecoins, ESMA's role is more centered on market integrity and investor protection. ESMA's responsibilities include:
Non-Stablecoin responsibilities: ESMA is responsible for overseeing investment tokens, utility tokens, and crypto-asset service providers (CASPs), while EBA focuses on asset-referenced tokens (ARTs) and e-money tokens (EMTs)
Market Surveillance: ESMA monitors the trading activities and market practices involving stablecoins to prevent market manipulation and ensure fair trading conditions.
Consumer Protection: ESMA implements measures to protect consumers from fraudulent schemes and misleading information related to stablecoin investments.
Regulatory Harmonization: ESMA works towards harmonizing regulatory practices across EU member states, ensuring a consistent approach to the supervision and regulation of stablecoins.
Why Regulate Stablecoins?
The regulatory interest in stablecoins stems from several critical factors:
Financial Stability: Stablecoins, due to their peg to traditional assets like fiat currencies, have the potential to impact financial stability. Large-scale adoption without adequate regulatory oversight could lead to systemic risks.
Consumer Protection: Given the growing popularity of stablecoins, there is an increased risk of consumers being exposed to fraudulent schemes and financial losses. Regulatory frameworks aim to protect consumers by ensuring transparency and reliability.
Market Integrity: Stablecoins are integral to the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem, often used in trading and as collateral in various financial activities. Regulating stablecoins helps maintain market integrity and prevent abuses such as market manipulation.
Preventing Illicit Activities: The anonymous nature of cryptocurrency transactions makes them susceptible to money laundering and other illicit activities. Regulatory oversight helps mitigate these risks by imposing stringent compliance requirements.
Conclusion
The MiCA regulation marks a significant advancement in the EU's approach to regulating stablecoins, ensuring that these digital assets are safe, reliable, and transparent. The EBA and ESMA play crucial roles in enforcing these regulations, each focusing on different aspects of stability and market integrity. By regulating stablecoins, authorities aim to protect consumers, maintain financial stability, and prevent illicit activities, ultimately fostering a more secure and trustworthy cryptocurrency market.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and compliant with these regulations is essential for all participants in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
8 The Green
19901 City of Dover
Delaware
United States
www.payrate42.com
PayRate42 is a rating agency specializing in payment processors. Our main goal is to protect merchants and consumers by providing transparency through the evaluation and rating of financial service providers. High-Risk Payment Processors (HRPP) operating outside the established regulatory framework are our primary focus.
MiCA and Stablecoins: An Overview
MiCA aims to provide a comprehensive regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies and digital assets within the EU, enhancing market integrity and consumer protection. Stablecoins, classified under MiCA as either asset-referenced tokens (ARTs) or e-money tokens EMTs), face specific regulatory requirements to ensure their stability and reliability. These requirements include maintaining sufficient reserves, regular audits, transparency in operations, and adherence to consumer protection standards.
Roles of EBA and ESMA
EUROPEAN BANKING AUTHORITY (EBA)
The EBA plays a pivotal role in the supervision of significant stablecoins - ARTs and EMTs - under MiCA. When stablecoins surpass a specific adoption threshold, determined by quantitative and qualitative indicators, they fall under the direct supervision of the EBA rather than national authorities. The EBA's responsibilities include:
Ensuring Adequate Reserves: The EBA ensures that stablecoin issuers maintain adequate reserves to back the value of their tokens, safeguarding against insolvency risks.
Conducting Audits: Regular audits are mandated to verify the integrity of the stablecoin reserves and operational practices.
Enforcing Transparency: The EBA requires issuers to provide detailed reports and disclosures, promoting transparency and protecting investors.
EUROPEAN SECURITIES AND MARKETS AUTHORITY (ESMA)
While the EBA focuses on the financial stability and reserve management of stablecoins, ESMA's role is more centered on market integrity and investor protection. ESMA's responsibilities include:
Non-Stablecoin responsibilities: ESMA is responsible for overseeing investment tokens, utility tokens, and crypto-asset service providers (CASPs), while EBA focuses on asset-referenced tokens (ARTs) and e-money tokens (EMTs)
Market Surveillance: ESMA monitors the trading activities and market practices involving stablecoins to prevent market manipulation and ensure fair trading conditions.
Consumer Protection: ESMA implements measures to protect consumers from fraudulent schemes and misleading information related to stablecoin investments.
Regulatory Harmonization: ESMA works towards harmonizing regulatory practices across EU member states, ensuring a consistent approach to the supervision and regulation of stablecoins.
Why Regulate Stablecoins?
The regulatory interest in stablecoins stems from several critical factors:
Financial Stability: Stablecoins, due to their peg to traditional assets like fiat currencies, have the potential to impact financial stability. Large-scale adoption without adequate regulatory oversight could lead to systemic risks.
Consumer Protection: Given the growing popularity of stablecoins, there is an increased risk of consumers being exposed to fraudulent schemes and financial losses. Regulatory frameworks aim to protect consumers by ensuring transparency and reliability.
Market Integrity: Stablecoins are integral to the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem, often used in trading and as collateral in various financial activities. Regulating stablecoins helps maintain market integrity and prevent abuses such as market manipulation.
Preventing Illicit Activities: The anonymous nature of cryptocurrency transactions makes them susceptible to money laundering and other illicit activities. Regulatory oversight helps mitigate these risks by imposing stringent compliance requirements.
Conclusion
The MiCA regulation marks a significant advancement in the EU's approach to regulating stablecoins, ensuring that these digital assets are safe, reliable, and transparent. The EBA and ESMA play crucial roles in enforcing these regulations, each focusing on different aspects of stability and market integrity. By regulating stablecoins, authorities aim to protect consumers, maintain financial stability, and prevent illicit activities, ultimately fostering a more secure and trustworthy cryptocurrency market.
As the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and compliant with these regulations is essential for all participants in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
8 The Green
19901 City of Dover
Delaware
United States
www.payrate42.com
PayRate42 is a rating agency specializing in payment processors. Our main goal is to protect merchants and consumers by providing transparency through the evaluation and rating of financial service providers. High-Risk Payment Processors (HRPP) operating outside the established regulatory framework are our primary focus.
Permanent link to this press release:
Copy
Please set a link in the press area of your homepage
to this press release on woodPRI. woodPRI disclaims liability for any content contained in
this release.
Recommend
/newsMicroencapsulation Market Deep Analysis on Key Players - Dow Corning, Encapsys, Syngenta Crop Protection, Evonik Industries, 3M and Bayer
Market Study Report Adds Global Microencapsulation Market Size, Status and Forecast 2024 added to its database. The report provides key statistics on the current state of the industry and other analytical data to understand the market.
Extensive research is required for choosing the appropriate cor...

/newsGermany Airbag Market Size 2023: Global Share, Industry And Report Analysis By 2030 | Hyundai Mobis Co., Ltd. Key Safety Systems, Inc. Robert Bosch GmbH
Germany airbag market is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 6% during the forecast period. Germany Airbag Market research report refers to gathering and analyzing significant market data serve as best medium for various industry players to launch novel product or service. It is vital for key firms...
/newsSecurities Brokerages And Stock Exchanges Market Outlook 2021: Big Things are Happening
A new intelligence report released by HTF MI with title "Global Securities Brokerages And Stock Exchanges Market Survey & Outlook" is designed covering micro level of analysis by Insurers and key business segments, offerings and sales channels. The Global Securities Brokerages And Stock Exchange...

/newsRenewable Chemicals Market Emerging Trends and Competitive Landscape Forecast to 2028
The renewable chemicals market was valued at US$ 80,566.30 million in 2021 and is projected to reach US$ 1,76,750.76 million by 2028 it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.9% from 2021 to 2028. The research report focuses on the current market trends, opportunities, future potential of the market, a...
/newsHow Coronavirus is Impacting Cold Brew Coffee, Global Market Volume Analysis, Size, Share and Key Trends 2020-2026
"Market Latest Research Report 2020:
Los Angles United States, February 2020: The Cold Brew Coffee market has been garnering remarkable momentum in the recent years. The steadily escalating demand due to improving purchasing power is projected to bode well for the global market. QY Research's lates...
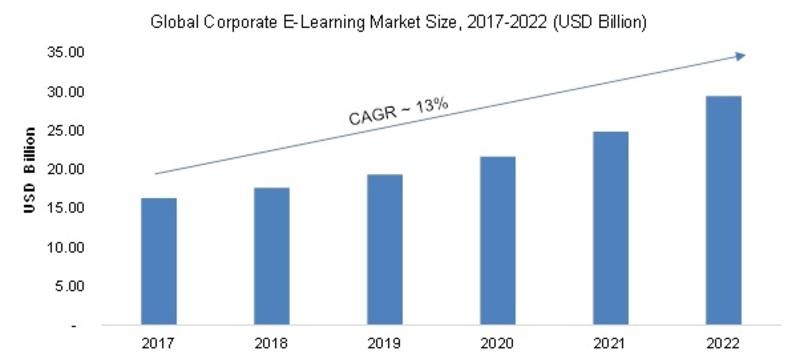
/newsCorporate E-Learning Market - Global Industry Size, Share, Key Players Analysis that are Infor, SkillSoft Corporation, Adrenna, CERTPOINT Systems and others with Regional Forecast to 2022
Overview:
E-Learning is used to enhance the learning procedures for newer job requirements and to make employees sound about the internal and external changes in the market and respective organizations. This method has created considerable differences in the ways of training and developing employee...
